MCB – handling guidance1
Kabiven (amino acids, electrolytes, glucose, lipid emulsion) has been used for illustration purposes.
The information in this section applies to all the Fresenius Kabi multi-chamber product ranges.
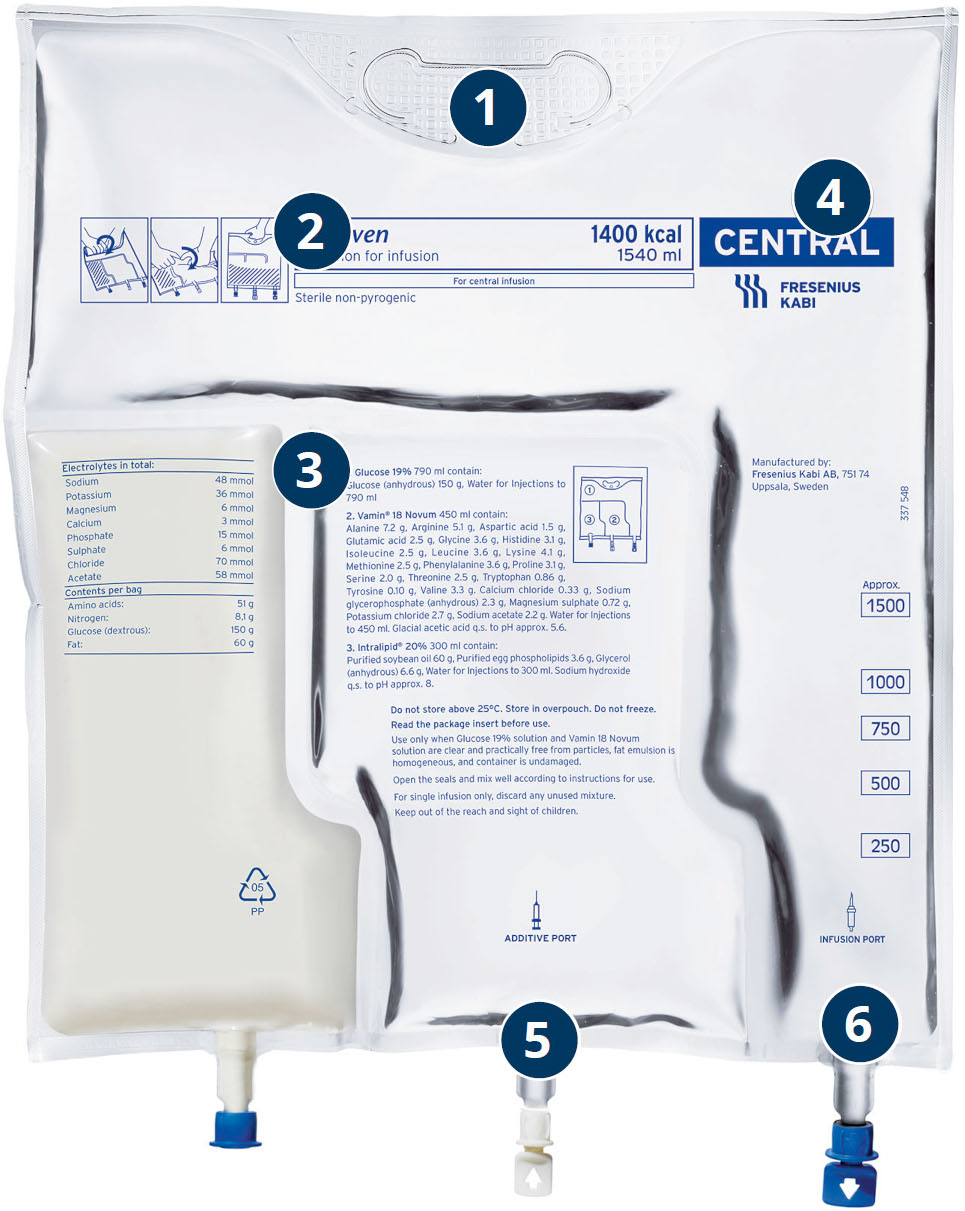
- Hanging Hole
- Bag Name
- Bag Content
- Route of Administration
- Additions Port
- Administration Port
Note: The handling guidance section of this website is to demonstrate technique only. Please ensure you adhere to your local policy for handling parenteral nutrition products, including observing aseptic technique.
Remove the overpouch
- Place the bag on a clean, flat surface
- Tear from the notch close to the ports along the portside edge
- Discard the overpouch and the oxygen absorber
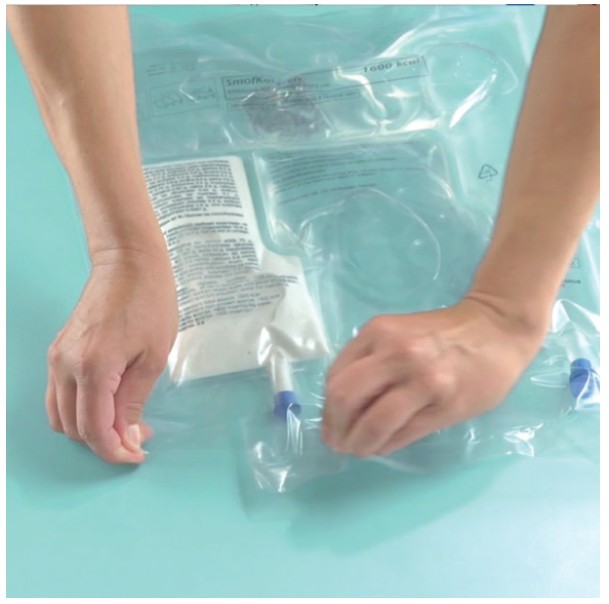
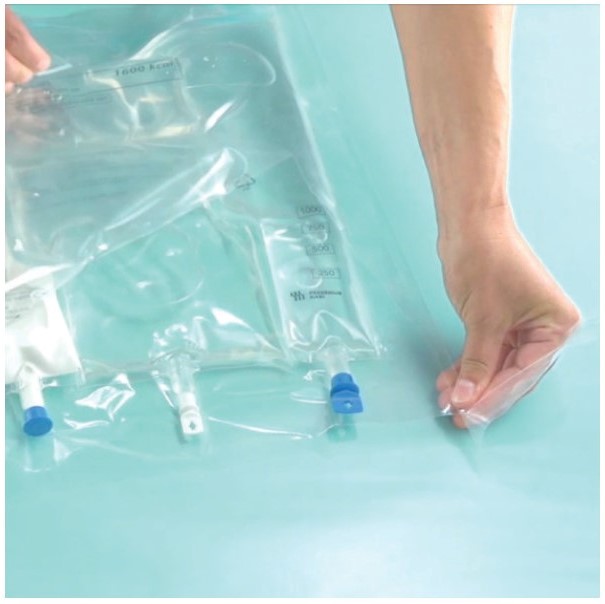


Open the peel seals*†
- Place the bag on a clean, flat surface, again with the text side up and the ports pointing away
- Starting from the right-hand corner, roll the bag tightly with the right hand (A)
- Roll straight and apply constant pressure with the knuckles on your left hand until the first seal (B) and then the second seal (C) breaks
- Continue rolling until the peel seals have opened all the way down to the port seal
- Repeat steps 2 to 4 to open second peel seal if necessary
Note: Do not open horizontal seal.
* For your information: The peel seals can also be opened before removing the overpouch.
† Never pull the peel seals apart like a crisp packet.
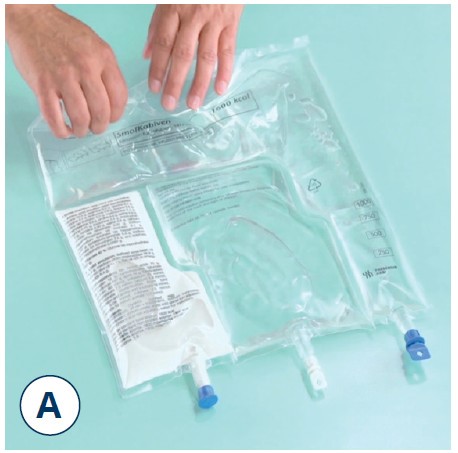
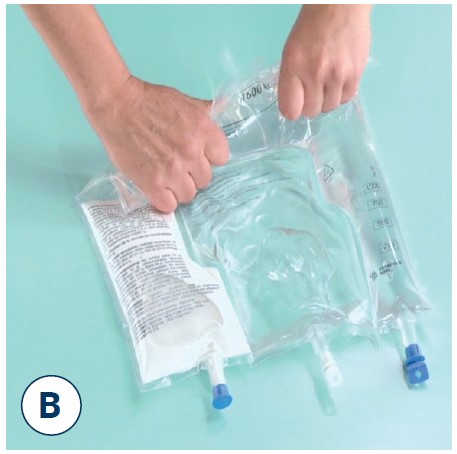
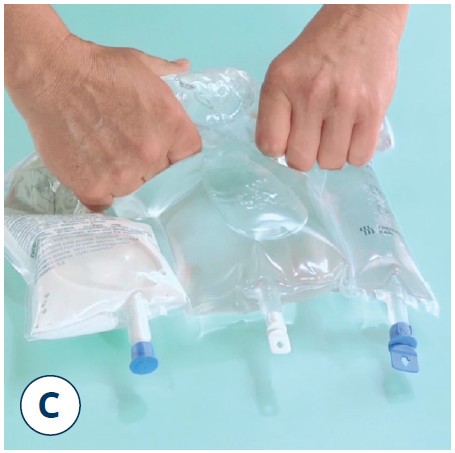
Mix thoroughly
- Take hold of the bag with both hands
- Turn the bag upside down and then return to the original position
- Repeat step 2 twice more
Note: Make sure the fluid passes around the unopened horizontal peel seal whilst inverting the bag.
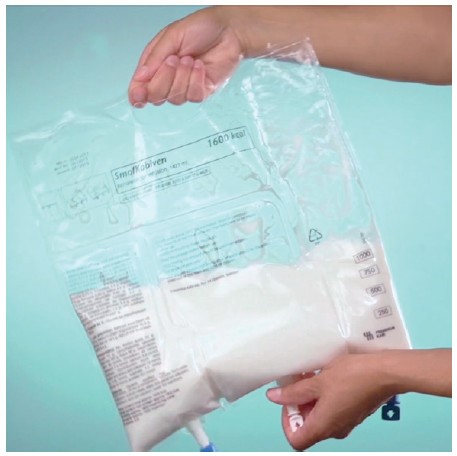
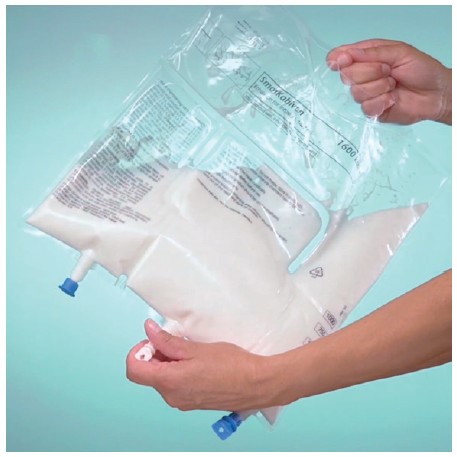


Note: The 2 vertical peel seals need to be broken. The horizontal peel seal does NOT need to be broken.
Please ensure you observe your local policies and procedures for the handling of parenteral nutrition products.
Content for demonstration of technique only. Please ensure you adhere to your local policy for handling products for parenteral nutrition, including observing aseptic technique.
Making additions1
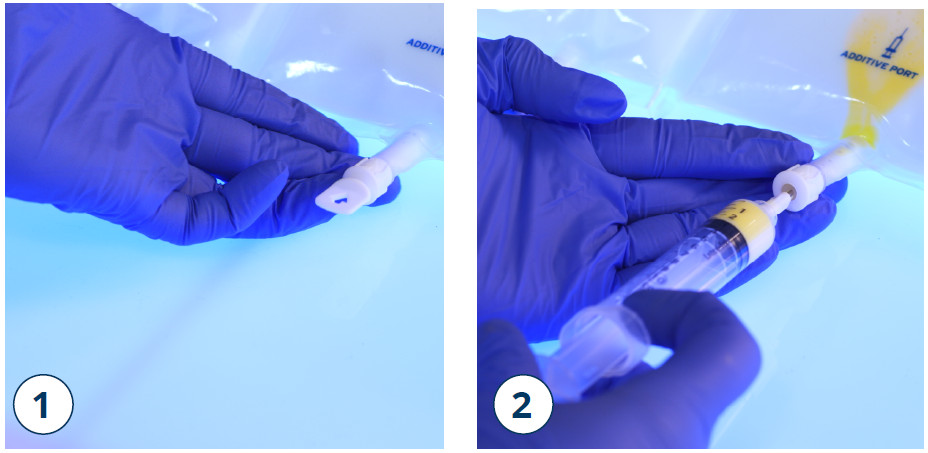
- Place the bag on a flat surface again. Shortly before injecting the additives, break off the tamper-evident arrow flag from the white additive port (1)
Note: The membrane of the additive port is sterile.
- Hold the base of the additive port. Insert the needle, inject the additives (with known compatibility) through the centre of the injection site (2)
- Mix throughly between each addition by inverting the bag three times
- Use syringes with needles of 18–23 gauge and a length of max. 40 mm
This is for general guidance only, ensure you follow your local policy for handling products for parenteral nutrition and intravenous use. As according to the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC), additions should only be made when compatibility has been documented and confirmed.
Additions should only be made:
- using aseptic technique
- when the three chambers of the bag have been mixed
See Summaries of Product Characteristics or contact Fresenius Kabi Medical Information on 01928 533575 for further information.
Inserting the infusion set
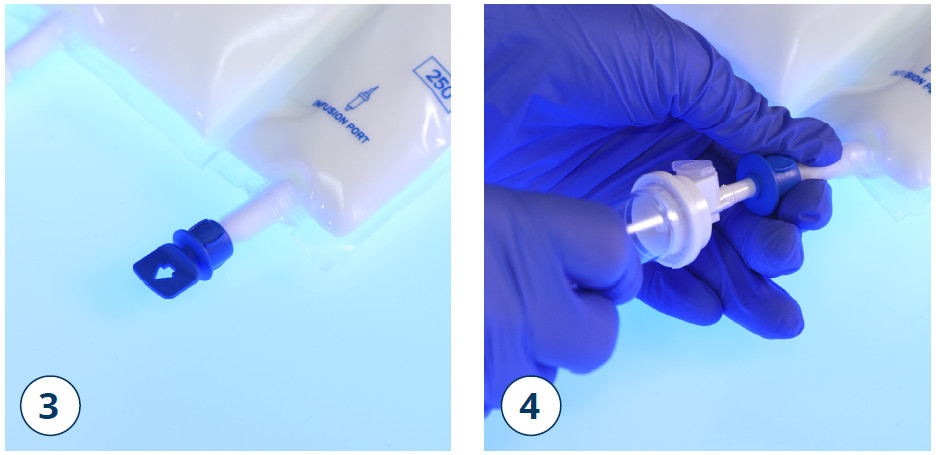
- Shortly before inserting the infusion set, break off the tamper-evident arrow flag from the blue infusion port (3)
Note: The membrane of the infusion port is sterile.
- Use a non-vented infusion set or close the air-inlet on a vented set
- Hold the base of the infusion port
- Push the spike through the infusion port
- The spike should be fully inserted to secure it in place (4)
Hanging the bag

- Hang the bag up by the hole below the handle. Alternatively, a special metal hanger can be used.
Information at a glance: ports and seals*1
Key benefits of the ports
- The additive and infusion port membranes are sterile, thus enabling use without disinfection
- The port membranes are self-sealing
- The additive and infusion ports are latex-free
Key benefits of the peel seals
- Easy opening of the peel seals, thereby facilitating handling
Bag design*1
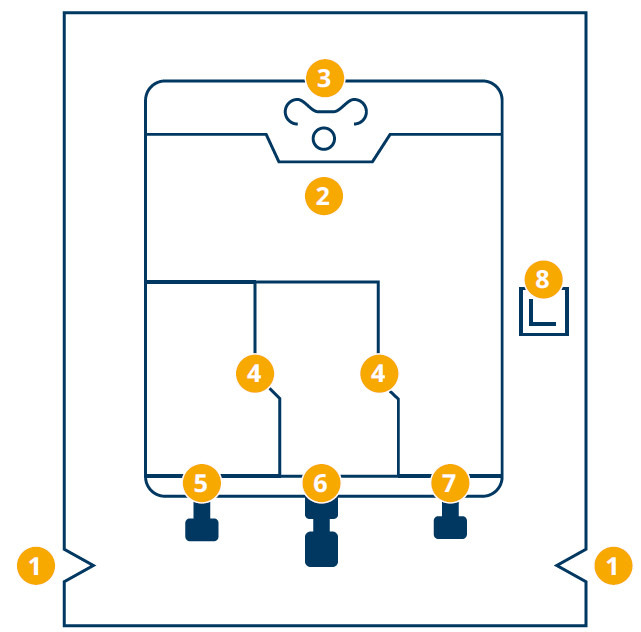
- Large notches in the over pouch – to simplify its removal
- Hole for hanging up the bag – the upper part of the bag guarantees a stable shape during infusion
- Handle – shape allows for comfortable carrying
- Peel seals – easy opening by rolling from the top downwards
- Blind port – only used for filling
- Additive port – sterile membrane
- Infusion port – sterile membrane
- Oxygen absorber – to eliminate any remaining oxygen
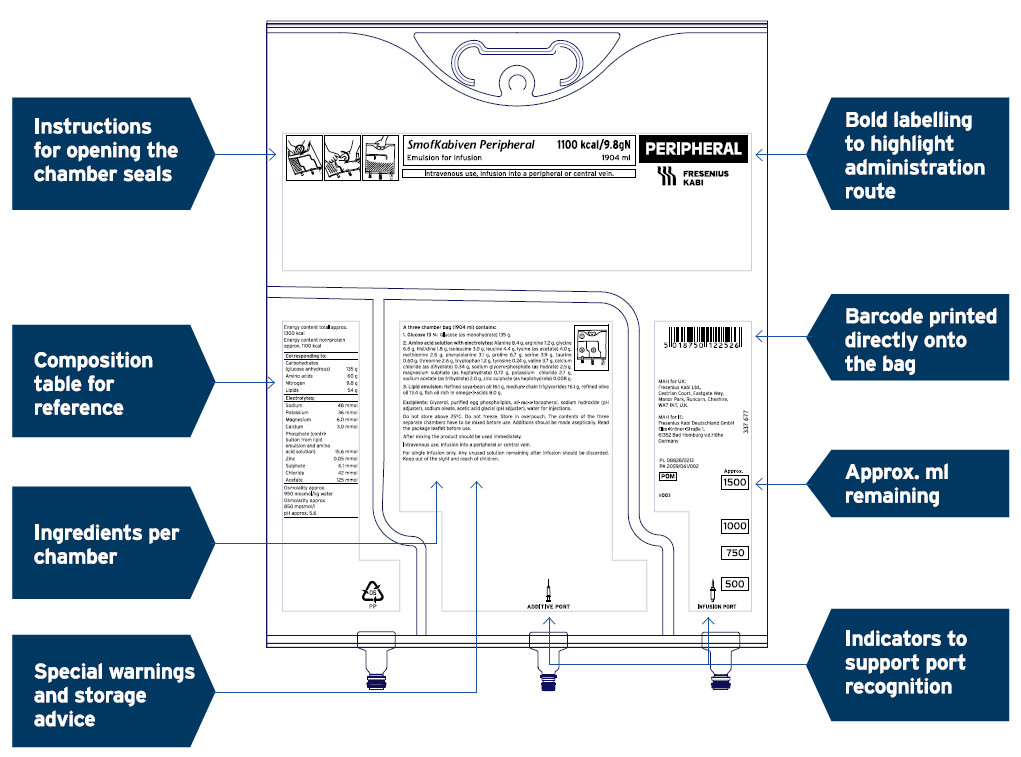
MCB – label redesign2
Fresenius Kabi has refreshed the label design of its MCB portfolio. The revised design features will be harmonised throughout our ranges and have been designed to support the user experience. Safety and user convenience are our priority, and the revised labels include features such as:
- Bold labelling to highlight products for central or peripheral administration
- Colour differentiation between central and peripheral bags
- Barcodes printed directly onto the bags
- Instructions for opening the chamber seals
- Composition tables and ingredients listed for each chamber. The re-designed labels will be implemented in phased approach across the MCBs range
Redesigned to support improved user experience2
SmofKabiven Peripheral (amino acids, electrolytes, glucose, lipid emulsion) and SmofKabiven Central (amino acids, electrolytes, glucose, lipid emulsion) have been used for illustration purposes.
Different colours and bold printing to highlight the route of administration2
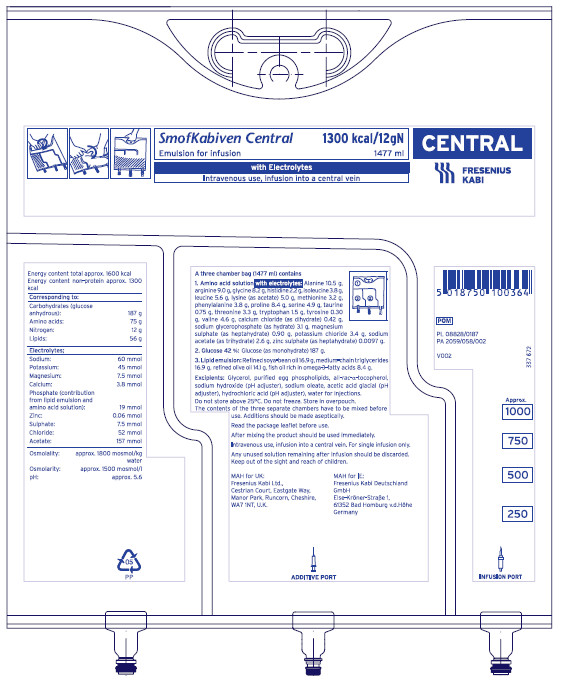
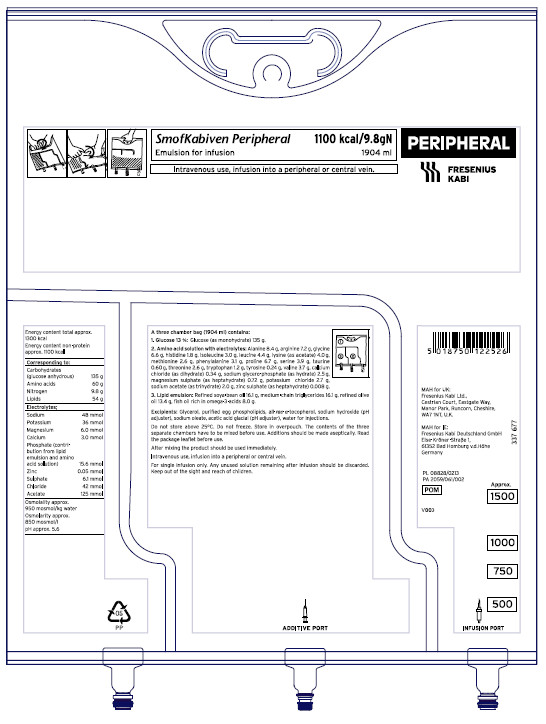
Note: Products labelled as peripheral may be administered via peripheral or central routes – check product label or summary of product characteristics for more information).
Terminology for bags used in PN
What’s in a name?
There are a number of different names and terms, which are often used interchangeably when referring to PN bags, yet they have distinct practical differences. For example, the difference between a compounded standard bag and a compounded MCB.
Other names used to describe standardised PN include:
- Base bags
- Base bags with additions
- Commercial pre-mixed
- Ready to use
- Made-to-stock (MTS)
SmofKabiven Low Osmo Peripheral (amino acids, electrolytes, glucose, lipid emulsion) and SmofKabiven Central (amino acids, electrolytes, glucose, lipid emulsion) have been used below for illustration purposes.
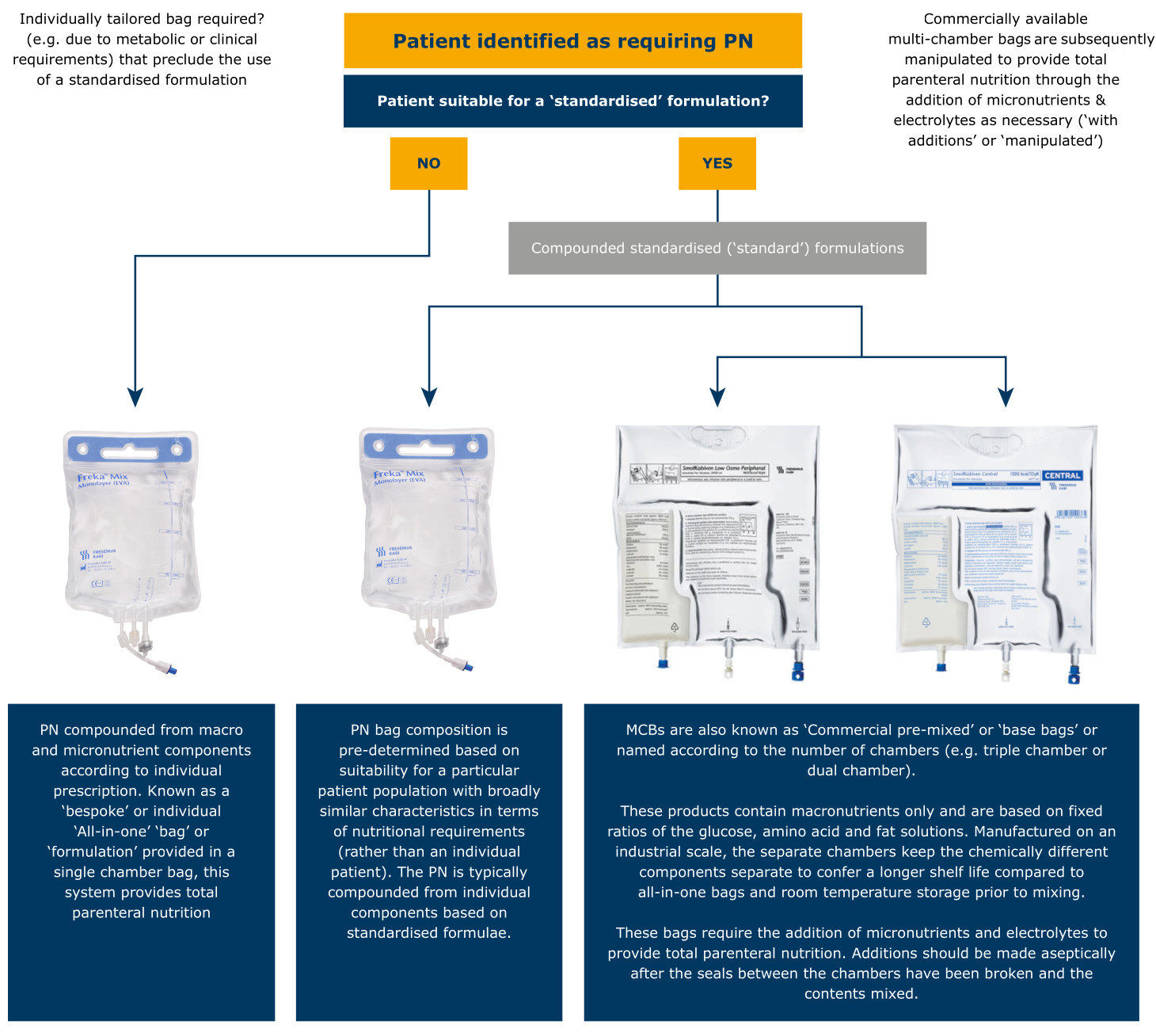
MCB = Multi-chamber bag; PN = Parenteral Nutrition